MicroMV 串口通信
MicroMV上的串口通讯
- UART对象
''' 初始化一个串口对象 uart_idx , 串口ID, 我们这里只能写1或者3 baud_rate , 波特率 ''' UART(uart_idx, baud_rate)
- 初始化UART对象
uart = UART(4, 115200)
- UART 函数操作
uart.read(10) # read 10 characters, returns a bytes object # 读入10个字符, 返回一个比特对象 uart.read() # read all available characters # 读取所有的有效字符 uart.readline() # read a line # 读入一行 uart.readinto(buf) # read and store into the given buffer # 读入并且保存在缓存中 uart.write('abc') # write the 3 characters # 向串口写入3个字符abc
- 单个字符的读取与写入
uart.readchar() # read 1 character and returns it as an integer # 读入一个字符 uart.writechar(42) # write 1 character # 写入ASCALL码为42的字符
- 判断串口是否有数据
uart.any() # returns the number of characters waiting
- 向串口发送数据的代码
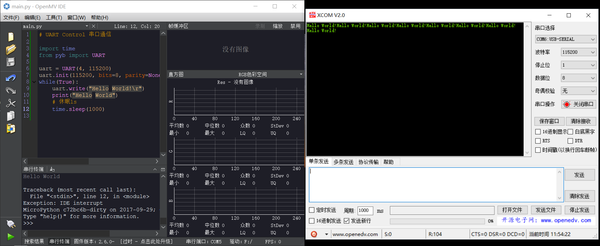
# UART Control 串口通信 import time from pyb import UART uart = UART(4, 115200) uart.init(115200, bits=8, parity=None, stop=1) # init with given parameters while(True): uart.write("Hello World!\r") print("Hello World") # 休眠1s time.sleep(1000)
- 实验效果
- TTL 转接到PC上的串口的显示效果
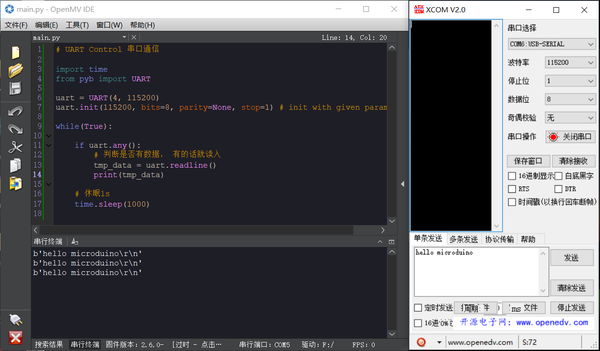
- 向串口接收数据
# UART Control 串口通信 import time from pyb import UART uart = UART(4, 115200) uart.init(115200, bits=8, parity=None, stop=1) # init with given parameters while(True): if uart.any(): # 判断是否有数据, 有的话就读入 tmp_data = uart.readline() print(tmp_data) # 休眠1s time.sleep(1000)
- 数据双向发送与接收
# UART Control 串口通信 import time from pyb import UART uart = UART(4, 115200) uart.init(115200, bits=8, parity=None, stop=1) # init with given parameters def sending_data(): global uart uart.write("haha\n") def recive_data(): global uart if uart.any(): tmp_data = uart.readline() uart.write("RECIVED : %s\n"%tmp_data) print(tmp_data) while(True): sending_data() recive_data() time.sleep(1000)