“Microduino-GPS”的版本间的差异
(→Pin Description) |
(→FQA) |
||
| (未显示2个用户的20个中间版本) | |||
| 第4行: | 第4行: | ||
| | | | ||
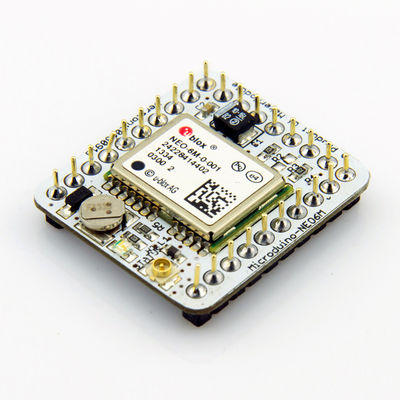
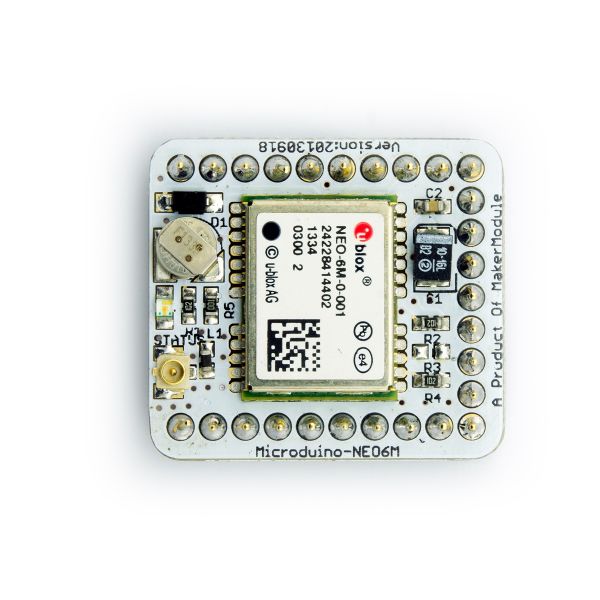
[[file:Microduino-NEO-rect.jpg|400px|thumb|right|Microduino-NEO]] | [[file:Microduino-NEO-rect.jpg|400px|thumb|right|Microduino-NEO]] | ||
| − | + | This probably the most beautiful GPS module you've seen, adopting UBLOX NEO-6M as it core with high sensitivity and update rate up to 5Hz. Besides, it owns a mini ceramic antenna with IPEX interface as well as a rechargeable backup battery. | |
| − | |||
==Feature== | ==Feature== | ||
| − | *High | + | *High sensitivity |
| − | *Update rate up to | + | *Update rate up to 5Hz |
| − | * | + | *Own a powerful PC support: u-center; |
| − | *PPS | + | *With PPS indicator, it is very convenient for us to judge the current status of the module; |
| − | * | + | *Own a built-in rechargeable backup battery(support warm or hot start); |
| − | *Small, cheap, stackable | + | *Small, cheap, stackable and open; |
| − | *Open | + | *Open hardware circuit design and Arduino compatible programming development environment; |
| − | * | + | *Uniform Microduino interface standard and rich peripheral modules, capable of having a fast and flexible connection and extension with other modules and sensors in accord with Microduino interface standard; |
| − | *2. | + | *Easy to be integrated to pegboards with a 2.45-pitch female header connector interface. |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |||
==Specifications== | ==Specifications== | ||
*Communication protocol: | *Communication protocol: | ||
| − | **Microduino NEO-6M module | + | **Microduino NEO-6M module adopts NMEA-0183 protocol to output GPS data and is capable of configuring modules through UBX protocol. |
| − | * | + | *Receiving characteristics |
| − | ** | + | **Channel 50,GPS L1(1575.42Mhz) C/A 码,SBAS:WAAS/EGNOS/MSAS |
**Capture tracking sensitivity:-161dBm | **Capture tracking sensitivity:-161dBm | ||
| 第31行: | 第30行: | ||
*Update rate | *Update rate | ||
| − | ** | + | **The maximum rate of 5Hz |
*Capture time | *Capture time | ||
| − | **cold | + | **cold start:27S(Shortest time) |
**warm start:27S | **warm start:27S | ||
**hot start:1S | **hot start:1S | ||
*Note: | *Note: | ||
| − | **Cold start | + | **Cold start refers to restarting when the history GPS information saved by the module all gets lost.(Equal to both of the main power supply and the backup battery run out of power.) |
| − | **Warm start | + | **Warm start refers to restarting when the module the current satellite information disaccords with the history GPS receiving information saved by the module. |
| − | **Hot start means | + | **Hot start means restarting when the history GPS receiving information is saved by the module and keeps consistent with the current visible satellite information. |
*Interface characteristics | *Interface characteristics | ||
| − | ** | + | **TTL,3.3V/5V microcontroller system compatible |
**Serial communication baud rate: | **Serial communication baud rate: | ||
| − | ***Microduino NEO-6M module supports several baud rate:4800,9600,38400(defult),57600; | + | ***Microduino NEO-6M module supports several kinds of baud rate:4800,9600,38400(defult),57600; |
| − | * Set | + | * Set baud rate according to two resistors of the module (R3 and R4. 1k recommended): |
{|class="wikitable" | {|class="wikitable" | ||
! rowspan="1" | R3 || R4 || Protocol || Baud rate | ! rowspan="1" | R3 || R4 || Protocol || Baud rate | ||
| 第65行: | 第64行: | ||
! rowspan="1" | GPS Module Pin || Microduino Pin|| Function | ! rowspan="1" | GPS Module Pin || Microduino Pin|| Function | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | TX || RX0(or D2) || | + | | TX || RX0(or D2) || Sending pin of the module serial port (TTL level), capable of connecting to microcontroller's RXD |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | RX || TX1(or D3) || | + | | RX || TX1(or D3) || Receiving pin of the module serial port (TTL level), capable of connecting to microcontroller's MCU TXD |
|} | |} | ||
| 第80行: | 第79行: | ||
===Main components=== | ===Main components=== | ||
*GPS module:UBLOX NEO-6M:'''[[File:NEO-6 DataSheet (GPS.G6-HW-09005).pdf]]''' | *GPS module:UBLOX NEO-6M:'''[[File:NEO-6 DataSheet (GPS.G6-HW-09005).pdf]]''' | ||
| − | * | + | *Supercapacitor:XH414H '''[[File:XH414H.pdf]]''' |
*NMEA-0183 protocol: '''[[File:NMEA-0183 CN.pdf]]''','''[[File:NMEA-0183 EN.pdf]]''' | *NMEA-0183 protocol: '''[[File:NMEA-0183 CN.pdf]]''','''[[File:NMEA-0183 EN.pdf]]''' | ||
| 第86行: | 第85行: | ||
==Development== | ==Development== | ||
| − | * | + | * Please first make sure the +3.3 v power supply current can reach 200ma. (Using FT232R to debug directly is not recommended for the electric current is too small.) |
| − | * We suggest | + | * We suggest using Microduino Core32u4 to debug the Neo-6m module: |
| − | ** 32u4 module can use the USB to simulate | + | ** 32u4 module can make use of the USB port to simulate 0(Serial) and Neo-6m uses the Core32u4's serial 1 (RX0,TX1). So you don't need to change the existing jumper (RX0,TX1) and it won't impact the program downloading and the serial's function. |
| − | * Microduino | + | * Microduino Neo-6m uses the default serial RX0,TX1 to communicate with Core module, so it can not connect with Microduino FT232 directly. |
===Use PC to debug=== | ===Use PC to debug=== | ||
* Use serial directly: | * Use serial directly: | ||
| − | ** No need | + | ** No need to stack the FT232 directly and just cross connect the FT232 and NEO-6M's RX0,TX1. |
| − | ===Use | + | ===Use FT232R and Core to download and debug=== |
| − | * | + | *If you keep using the default jumper (RX0、TX1): |
| − | ** | + | **Please unplug the Microduino NEO-6M during the program download; |
| − | *If you want to change the | + | *If you want to change the jumpers to meet your requirement:Just cut the connection between the middle of two groups of pads and RX0/TX1,then connect them to D2, D3. |
| − | **If | + | **If you change the jumper, you need to change the serial connection between Microduino NEO-6M and Microduino Core from "TX-RX0、RX-TX1" to: |
| − | ***TX-D2、RX-D3 (For Core+'s | + | ***TX-D2、RX-D3 (For Core+'s Serial port) |
| − | ===Arduino library and | + | ===Arduino library and support package=== |
| − | * | + | *Microduino_GPS:https://github.com/Microduino/Microduino_Tutorials/tree/master/Microduino_Libraries/_05_Microduino_GPS |
| − | * | + | *Microduino_OLED_U8glib:https://github.com/Microduino/Microduino_Tutorials/tree/master/Microduino_Libraries/_01_Microduino_OLED_U8glib |
*[http://www.u-blox.com/en/evaluation-tools-a-software/u-center/u-center.html u-center-8.0] | *[http://www.u-blox.com/en/evaluation-tools-a-software/u-center/u-center.html u-center-8.0] | ||
| 第111行: | 第110行: | ||
===How to use the library=== | ===How to use the library=== | ||
*For Adafruit_GPS library: | *For Adafruit_GPS library: | ||
| − | **Make sure the | + | **Make sure the baud rate of the GPS is 38400 in function "void setup()",that is:GPS.begin(38400); |
**If you don't change the jumper cable: | **If you don't change the jumper cable: | ||
***Unplug the Microduino NEO-6M module when downloading program; | ***Unplug the Microduino NEO-6M module when downloading program; | ||
| − | *** | + | ***When you use the Core or Core+ to debug, please make sure that the program is defined as "Adafruit_GPS GPS(&Serial)"; |
**If you have changed the jumper cable: | **If you have changed the jumper cable: | ||
| − | ***When use Core+ to | + | ***When you use Core+ to debug,please make sure that the program is defined as "Adafruit_GPS GPS(&Serial1)"; |
| − | ***When use Core to debug, make sure | + | ***When you use Core to debug, please make sure that the program is defined as "SoftwareSerial mySerial(3, 2)" and "Adafruit_GPS GPS(&mySerial)"; |
| − | ===PPS | + | ===PPS Status indicator=== |
| − | * | + | *The indicator is connected to the TIMEPULSE port of the UBLOX NEO-6M module and the output characteristics of the port can be set by the program; |
| − | *PPS | + | *The PPS indicating light has two status under the default condition(without program setup): |
| − | ** | + | **Always keeping on means that the indicator has started work but failed to achieve positioning; |
| − | ** | + | **Keeping flashing means the module has achieved positioning. |
| − | * | + | *By the PPS indicator, it is very easy for us to judge the current status of the module. |
==Application== | ==Application== | ||
===Download program=== | ===Download program=== | ||
| − | + | Test Program:'''[[File:Program Test NEO-6M.zip]]''' | |
| − | ===Test Microduino NEO-6M | + | ===Test Microduino NEO-6M=== |
| − | * | + | *Hardware:Microduino FT232R,Microduino Core,Microduino OLED and Microduino NEO-6M; |
| − | * | + | *Software:Arduino IDE(version 1.0 and higher), Adafruit_GPS library and Microduino test program(Arduino part); |
| − | *Test environment:Open | + | *Test environment:Open area; |
| − | *Put the downloaded library | + | *Put the downloaded library into libraries of the Arduino IDE installation folder; |
| − | *Start Arduino IED,open the test | + | *Start Arduino IED,open the test program,choose "Microduino Core (Atmega328P@16M,5V)" and download directly; |
| − | * | + | *If using the default jumper pin (RX0,TX1): |
| − | **Unplug the Microduino NEO-6M module when downloading | + | **Unplug the Microduino NEO-6M module when downloading program;Since Microduino NEO-6M module has the same RX0/TX1 pin position with Microduino FT232R, the communication will be influenced if you stack these two modules together. |
| − | *After | + | *After the download, you'd better cut off the power supply firstly and then stack them for fear of causing short circuit. . |
| − | * | + | *Observe the OLED after the download is completed: |
| − | ** | + | **Data and time will be displayed half minute later; |
| − | ** | + | **Keep waiting. When you see the PPS indicator flashes, the index of the speed, latitude and longitude should be displayed. If not, please restart Microduino-Core. |
| − | * | + | *Players can change jumpers on the back of the module:Cut off the connection between the middle of the bonding pads and RX0/TX1, then weld the middle of the bonding pads to D2 and D3. The purpose of changing jumper is to download program easily. Once you change the jumper, you superimpose three boards together to download program. |
| − | **If you use the | + | **If you use the changed jumper connection method, it will change the serial connection from TX-RX0,RX-TX1 to TX-D2,RX-D3 between Microduino NEO-6M and Core. |
===Test Mocroduino NEO-6M using PC=== | ===Test Mocroduino NEO-6M using PC=== | ||
| 第149行: | 第148行: | ||
There are two connection methods: | There are two connection methods: | ||
1. Use the default pin (RX0、TX1): | 1. Use the default pin (RX0、TX1): | ||
| − | *You need the Microduino FT232R module to connect the PC, but can't superimpose the FT232R, NEO-6M and Core module directly. Because the FT232 and NEO-6M has the same RX/TX defination and position on board, but the normal serial communication should be cross | + | *You need the Microduino FT232R module to connect the PC, but can't superimpose the FT232R, NEO-6M and Core module directly. Because the FT232 and NEO-6M has the same RX/TX defination and position on board, but the normal serial communication should be cross connected with RX/TX. |
| − | ** | + | **Stack up the FT232 and microduino core, then conect them to PC with microUSB to download program; |
| − | ** | + | **Use jumpers to cross connect the RX0/TX1 of FT232 and NEO-6M, that is to connect the RX0 of NEO-6M to the TX1 of FT232, and the TX1 of NEO-6M to RX0 of FT232. |
| − | **Connect the 3V3 pin of NEO-6M module to 3V3 pin of FT232 | + | **Connect the 3V3 pin of NEO-6M module to 3V3 pin of FT232 and GND to GND for modules' power supply. |
[[File:Neo-6m debugging.jpg|thumb|400px|center|crossover configuration]] | [[File:Neo-6m debugging.jpg|thumb|400px|center|crossover configuration]] | ||
2. Use the changed jumper mode | 2. Use the changed jumper mode | ||
| − | If you have changed the jumper as | + | If you have changed the jumper as it describes above, you can stack up FT232, NEO-6M and Core module together, then connect to PC for debugging. |
====Use u-center configuration module to update rage==== | ====Use u-center configuration module to update rage==== | ||
| − | *Firstly, place the Microduino NEO-6M into an open area, and then | + | *Firstly, place the Microduino NEO-6M into an open area, and then connect it to PC through Microduino FT232R; |
*Start "u-center" software: | *Start "u-center" software: | ||
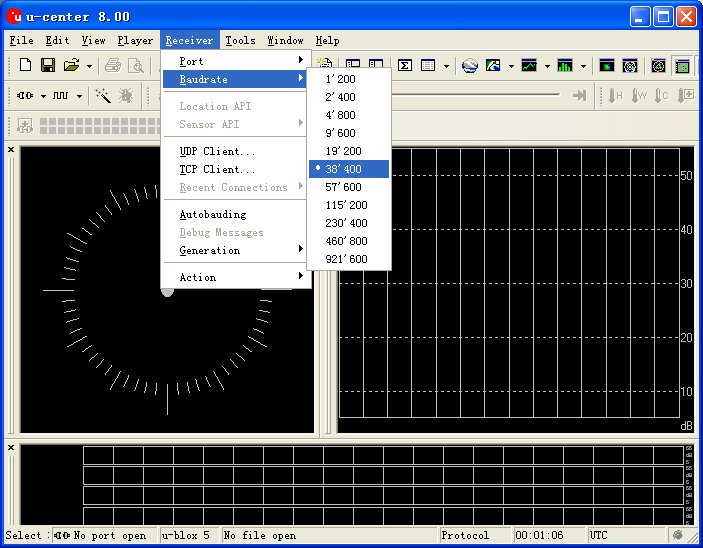
| − | **Set the baud | + | **Set the baud rate firstly:Menu:“Receiver”-“Baudrate”-“38400”; |
[[File:U-center 01.jpg|thumb|703px|center|set baud rate]] | [[File:U-center 01.jpg|thumb|703px|center|set baud rate]] | ||
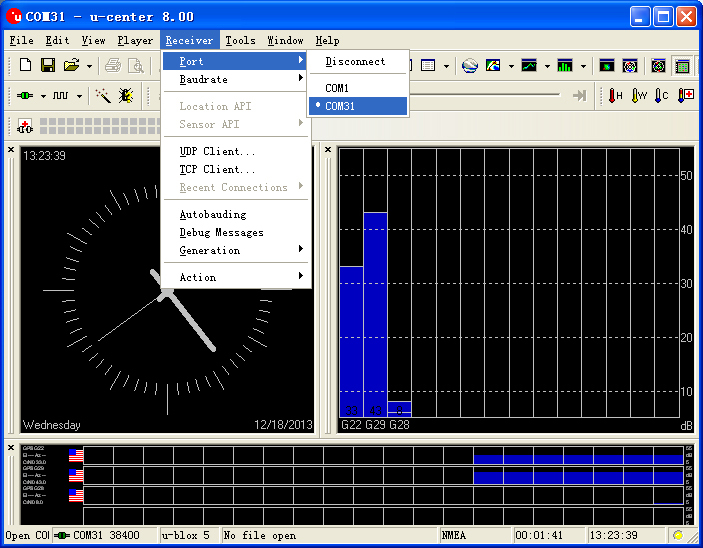
**Open the serial to start the communication:Menu:“Receiver”-“Port”- choose the port that Microduino FT232R using. | **Open the serial to start the communication:Menu:“Receiver”-“Port”- choose the port that Microduino FT232R using. | ||
| 第170行: | 第169行: | ||
*Update rate | *Update rate | ||
**Open menu:“View”-“Messages View”,display the "Messages" window; | **Open menu:“View”-“Messages View”,display the "Messages" window; | ||
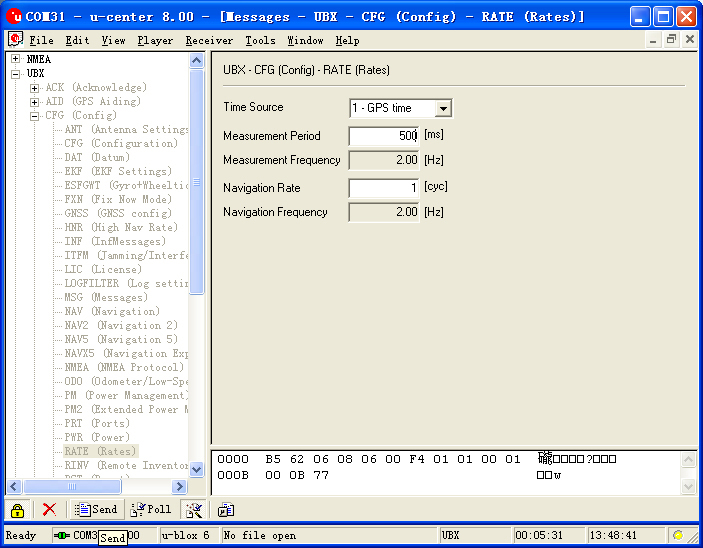
| − | **Open“UBX”-“CFG(Config)”-“RATE(Rates) | + | **Open“UBX”-“CFG(Config)”-“RATE(Rates)”,supposing you need 2HZ update rate, you just need to set the "Measurement Period" to 500ms; |
| − | **After | + | **After the configuration,just click the "Send" button on the bottom of the left and send the configuration to Microduino NEO-6M module. If the data update rate turns faster on other information window, that means the setup is successful. |
[[File:U-center 04.jpg|thumb|703px|center|Configure window]] | [[File:U-center 04.jpg|thumb|703px|center|Configure window]] | ||
| − | == | + | ==FQA== |
| + | *This module's issue, you can find the solution in wiki. Please refers to the wiki to test this module. | ||
| + | *If using the core and GPS module, what’s the power consumption? | ||
| + | **'''Make sure 3.3V with 200mA.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Buy== | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
2015年1月3日 (六) 03:51的最新版本
| Language | English |
|---|
|
This probably the most beautiful GPS module you've seen, adopting UBLOX NEO-6M as it core with high sensitivity and update rate up to 5Hz. Besides, it owns a mini ceramic antenna with IPEX interface as well as a rechargeable backup battery. 目录Feature
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Specifications
Pin Description
文件:NEO6M-Pinout-2.jpg Microduino-NEO6M-Pinout 文件:NEO6M-Pinout-1.jpg Microduino-NEO6M-Pinout DocumentEagle PCB 文件:Microduino-NEO6M.zip
Main components
Development
Use PC to debug
Use FT232R and Core to download and debug
Arduino library and support package
How to use the library
PPS Status indicator
ApplicationDownload programTest Program:文件:Program Test NEO-6M.zip Test Microduino NEO-6M
Test Mocroduino NEO-6M using PCConnection methodThere are two connection methods: 1. Use the default pin (RX0、TX1):
文件:Neo-6m debugging.jpg crossover configuration 2. Use the changed jumper mode If you have changed the jumper as it describes above, you can stack up FT232, NEO-6M and Core module together, then connect to PC for debugging. Use u-center configuration module to update rage
FQA
BuyHistoryPicture
Video |