“Microduino-Quadcopter Tutorial/ko”的版本间的差异
(Created page with "테스트") |
Shin SongSup(讨论 | 贡献) |
||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
| − | + | {| style="width: 800px;" | |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | ==개요== | ||
| + | *프로젝트: 마이크로두이노 쿼드콥터 | ||
| + | *목적 : 마이크로두이노 조이패드를 이용한 쿼드콥터 제어 | ||
| + | *난이도 : 높음 | ||
| + | *소요시간 : 6시간 | ||
| + | *메이커: 마이크로두이노 스튜디오 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==부품 리스트== | ||
| + | *마이크로두이노 | ||
| + | {|class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Module||Number||Function | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |마이크로두이노 코어||2||코어모듈 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |마이크로두이노 USBTTL ||1||프로그램 다운로드 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |마이크로두이노 10DOF ||1||위치제어 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |마이크로두이노 BT||2||무선통신 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |마이크로두이노 조이패드 ||1||리모트 컨트롤 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |마이크로두이노 TFT||1||디스플레이 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |마이크로두이노 쿼드콥터||1||4축 모터 드라이버 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | *기타 장비 | ||
| + | {|class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |USB 케이블 ||1||프로그램 다운로드 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ||쿼드콥터 프레임||1||Quadcopter Buildup | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |배터리||2||전원공급 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==참고문서== | ||
| + | *쿼드콥터 제어 프로그램 다운로드: | ||
| + | https://github.com/Microduino/Microduino_Tutorials/tree/master/Microduino_Advanced_Tutorial/Microduino_Joypad_QuadCopter/MultiWii | ||
| + | |||
| + | *MultiWiiConf PC 프로그램 다운로드 | ||
| + | https://github.com/Microduino/Microduino_Tutorials/tree/master/Microduino_Advanced_Tutorial/Microduino_Joypad_QuadCopter/MultiWiiConf | ||
| + | |||
| + | * PID 설정화일 다운로드 | ||
| + | https://github.com/Microduino/Microduino_Tutorials/tree/master/Microduino_Advanced_Tutorial/Microduino_Joypad_QuadCopter/%E9%85%8D%E7%BD%AE%E6%96%87%E4%BB%B6 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==소개== | ||
| + | ===비행원리=== | ||
| + | Quadcopter, also called a quadrotor helicopter, is similar to a helicopter, which can fly or be suspended in the air. Like a traditional helicopter, it adopts a main rotor to generate lift and a tail rotor to offset the torque generated by the main rotor (Namely head-locking). Different from that drive method, The diagonal motor of the quadcopter adopts the pros and cons propeller design. So it needs no extra framework to have heard-locking. As it is shown in the picture 1.1, the No. 1 and No. 3 propellers are a pair of diagonal pros and cons propellers, and the No. 2 and No.4 are another pair. When the rotational speed keeps the same, the torque generated by the pro propeller will offset the the torque generated by the cons propeller to keep the direction unchanged (As the arrow shows). In the schematic diagram, the most common quadcopter is the X-shaped. (There is also a kind of cross-like quadcopter, which is easy to recognize but has a poor mobility. ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_Introduction1.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Quadcopter can finish four basic motions including rise and fall, pitch, roll and yaw. Rise and fall means the aircraft goes up vertically. The rising process is achieved by four motors speeding up at the same time. So does the falling process. Pitch means the aircraft tilts forward or backward, which is achieved by speeding up the No.3 and No.4 motors. Roll is actually that the aircraft tilts leftwards or rightwards, achieved by speeding up the NO.2 and No. 3 motors. Yaw is the deviation of the aircraft’s head, which is achieved by speeding up the No. 2 and No.4 motors. Players can watch and have a better understanding during the process of installing and debugging the quadcopter. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===구조=== | ||
| + | The structure schematic diagram is shown below. The simplified system is consist of a remote control signal receiver, an aircraft controller and four motors. The remote control signal receiver converts the received signal to the format of PWM or PPM and send it the aircraft controller. The controller controls the four motors via PWM and achieves its expected motion according to the remote control signal it receives as well as the sensor value. It is necessary for the aircraft controller to contain the gyroscope and the accelerometer. The position of the quadcopter is calculated through the data acquired from the two sensors and controls the rotating rate through algorithm like PID after the calculation. Off cause, you can also locate the aircraft’s head adding an electronic compass and GPS to locate the quadcopter. To be simple, quadcopter is a closed-cycle control system with two loops--the bigger loop is input by a remote control receiver and the smaller one is input by the attitude sensor. | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_Introduction2.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | For general fixed-wing model aircraft, the controller is not that necessary and some player won’t install it on the fixed-wing model aircraft. Different from that, the quadcopter is an underactuated system with three degrees of freedom and four control input, which needs a control system to take charge. | ||
| + | Off cause, there are some tech details remaining to be designed in the process, such as the reading-in data of the sensor needed to be filtered and the PID algorithm of the pitch, roll and yaw acquired to be adjusted. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==효고ㅗ== | ||
| + | Microduino adopts the unique U-shaped 27Pin interface standard(UPIN-27) with compact size (25.4mm X 27.95 mm) just like a quarter. All modules can be stacked together through UPIN-27, delivered ready to plug in. | ||
| + | Microduino-Quadcopter only needs five functional modules and the 330 Rack Mont Kits recommended at the least to work. (Microduino-Core, Microduino-10DOF, Microduino-BT, Microduino-QuadCopter and Microduino-Joypad.) And you only need to stack them together, which is very simple. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==쿼드콥터 만들고 디버깅하기== | ||
| + | ===하드웨어 조립하기=== | ||
| + | {|class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Module||Number||Function | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Microduino-Core||1||Core board | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Microduino-USBTTL ||1||Program download | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Microduino-10DOF ||1||Attitude stabilization | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Microduino-BT||1||Wireless communication | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Microduino-QuadCopter||1||Four-axis drive | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Fixate the flight-control backplane on the main frame and set a forward direction before you do that. (The default forward direction of the flight-control backplane is the open end direction of the UPin interface.) | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_setup1.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Fixate the Microduino-Quadcopter on the main frame. | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_setup2.4.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Fixate the four motor arms on the main frame and in the process, set the head direction as follows: | ||
| + | Generally, we set the two orange rotors in the front and the other two black ones in the back so that we can tell the head direction by the color even when the aircraft flies far away. When doing this, you also need to pay attention to the right order of CW and CCW paddle.CW paddles are marked with an A on it and CCW paddles are marked with a B.CW paddles should be fixed at left-front and right-rear.CCW paddles should be fixed at right-front and left-rear. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_setup2.1.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Attention:The installation methods are shown as follows: | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_setup2.2.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_setup2.3.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Fixate the four motors on the main frame. | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_setup2.5.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then connect those connectors to the motherboard. Although we’ve tried our best to make sure everything’s good, it’s still recommend to check those wires--the white and red wires from motors should be connected to the pin marked with a cross(+).The following figure shows a finished work. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_setup3.1.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_setup3.2.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Make Connection between Two BT Modules=== | ||
| + | Since we build the wireless remote control through Bluetooth, that makes the two BT modules indispensable. As to the connection method, you can refer to: [[How to Connect two Microduino-BT modules together] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Download & Debug=== | ||
| + | Assemble Microduino-Core,Microduino-10DOF and Microduino-USBTTL on the motherboard as the following figure: | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_Software1.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Place the quadcopter on a flat surface then connect it to the computer via USB.Select | ||
| + | Microduino Core (Atmega328P@16M,5V) in the Arduino IDE,then download the program. | ||
| + | Run the config tool in the following path:MultiWiiConf\application.windows32\MultiWiiConf.exe | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_MultiWiiConf1.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Connect PC to Quadcopter=== | ||
| + | Click the RECONNECT button to connect.The raw data and some graphs should be shown if everything’s okay. | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_MultiWiiConf2.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Adjust the Sensor==== | ||
| + | Make sure the quadcopter is on a flat surface,then click the CALIB_ACC button to calibrate accelerometer.DO NOT move the quadcopter in 5 secs.Then click the CALIB_MAG button to calibrate magnetometer.In the coming 30secs,please grab your quadcopter and rotate it in every axis repeatedly. | ||
| + | Then click the WRITE button to save the data. | ||
| + | By clicking SELLECT SETTING,various parameters can be set,and the quadcopter’s status will be shown. | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_MultiWiiConf4.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Set PID Parameter==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The quadcopter use proportional-integral-derivative controller (PID controller) to control its movement. With a proper set of PID values,the quadcopter can fly smoothly and stably. We offer the sample PID config file,user can load it and fly the copter in a few minutes: click LOAD,then select file pkj.mwi to load the config file,finally click write to save. If you want to adjust the parameters yourself,just click on the green bar and hold it,then drag it left or right to adjust.For more info, please google Multiwii. | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_MultiWiiConf_PID.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Set Flight Mode==== | ||
| + | To enhance the experience,we recommend users set several flight modes.Different flight modes can be selected by toggle the switch on the remote.And by using different combinations many flight modes can be chosen.The recommended flight modes settings are shown as below.To set a flight mode,just toggle the switch as your wish and click on the mode you want(the cube).ANGLE mode is the most stable mode,starters can practice under this mode.Don’t forget to WRITE before unplug the quadcopter.For more info,please google Multiwii. | ||
| + | When everything’s done,remove the Microduino-USBTTL.[[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_MultiWiiConf_ANGLE.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Build & Debug the Remote Controller== | ||
| + | Here we adopt Microduino-Joypad as the remote controller. Off cause, you need modules, such as Microduino-TFT, Microduino-Core, Microduino-USBTTL and Microduino-BT to build the remote controller. | ||
| + | {|class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Module||Number||Function | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Microduino-Core||1||Core board | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Microduino-USBTTL ||1||Download program | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Microduino-BT||1||Wireless communication | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Microduino-Joypad ||1||Remote control | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Microduino-TFT||1||Display | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Hardware Buildup=== | ||
| + | *Step 1:Install Microduino-TFT on the panel of Microduino-Joypad; | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_Joypad_TFT.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Step 2: Fixate Microduino-Joypad with screws and stick the panel to the bottom of Microduino-Joypad; | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_Joypad_nilong.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Step 3; Connect Microduino-TFT and Microduino-Joypad through wires; | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_Joypad_Connection.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Step 4: Connect the Li-ion battery to the bottom of the base board and make sure a right connection of the positive and negative charges; | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_Joypad_power.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Step 5: Fix the base board and the panel with nylon screws; | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_Joypad_face_bord.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Step 6: You can start the power and see if it is charged normally. | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_Joypad_switch.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Step 7: Stack Microduino-USBTTL, Microduino-Core to the base of Microduino-Joypad. In the meantime, just don’t stack Microduino-BT module, or it will cause the serial port conflict. | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_Joypad_Module.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Debug the Software=== | ||
| + | *Download Microduino_Joypad_Ctrl program: | ||
| + | https://github.com/Microduino/Microduino_Tutorials/tree/master/Microduino_Advanced_Tutorial/Microduino_Joypad_QuadCopter/Microduino_Joypad_Ctrl | ||
| + | |||
| + | Meantime, you also need the libraries below: | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''_01_Microduino_TFT_GFX:''' | ||
| + | https://github.com/Microduino/Microduino_Tutorials/tree/master/Microduino_Libraries/_01_Microduino_TFT_GFX | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''_01_Microduino_TFT_ST7735 :''' | ||
| + | https://github.com/Microduino/Microduino_Tutorials/tree/master/Microduino_Libraries/_01_Microduino_TFT_ST7735 | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''_01_Microduino_TFT:''' | ||
| + | https://github.com/Microduino/Microduino_Tutorials/tree/master/Microduino_Libraries/_01_Microduino_TFT | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''_08_Microduino_Shield_Joypad:'''https://github.com/Microduino/Microduino_Tutorials/tree/master/Microduino_Libraries/_08_Microduino_Shield_Joypad | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Open Microduino_Joypad_Ctrl program and choose the right board for download after it is get compiled successfully. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Take off Microduino-USBTTL after the download, stack Microduino-BT and have an overall debugging at last. | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_Joypad_BT.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Test Fly== | ||
| + | === Debug Microduino-Joypad=== | ||
| + | *Start the remote controller, press the reset key and then enter the system. Please press the button A in 4 seconds and enter the adjustment mode. | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_Joypad_Remote1.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Rotate the two rockers at the maximum degree of 360 and you can enter B button if seeing no data change on the TFT screen, entering the flight mode. | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_Joypad_Remote2.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Turn the top-left switch downside(Close the throttle) and then pull the throttle lever to the bottom. | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_Joypad_Remote4.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Debug the Quadcopter Frame=== | ||
| + | *Make sure Microduino-BT stacked on the quadcopter for communicating with the remote controller. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Fix the battery at the bottom of the quadcopter and then connect with the power cord of Microduino-Quadcopter.(The red cord is the positive and the black one is the negative.) | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_Remote2.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Start Microduino-Quadcopter, put it on a stable area, press the reset key and the system will automatically adjust the sensors. When it is undone, the red LED light will blink on the board and will go off after the adjustment is done, waiting for unlock. | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_Remote3.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Overall Test=== | ||
| + | *Watch whether the Microduibno-BT module on the quadcopter is connected with the BT on the Joypad, which you can tell by the indicator of the BT module. When the indicator does not blink, it means the BT modules being connected. | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_Remote4.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Unlock the quadcopter and pull the top-left switch downside(Close the throttle) and adjust the throttle to the lowest before flying for fear that the throttle rocker value is too large and causes accident. Put the throttle to the bottom-right and you can see the LED blink, just be ready for connecting, wait for about 2 seconds and loose the throttle rocker. Repeat that operation for several times until the LED is on for a long time. But if you try that operation and still cannot unlock the quadcopter, please reset the quadcopter’s core and the system will adjust the sensors automatically, just try to unlock once again. | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_Remote5.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
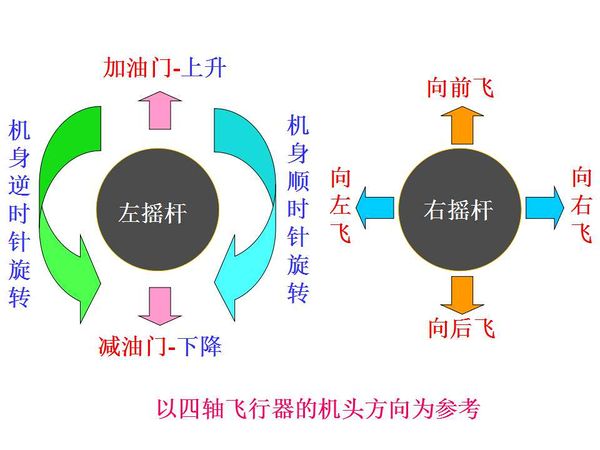
| + | *Pull the throttle rocker to the bottom, push the top-left switch upside(Open the switch of the throttle), at this time, you can refer to the rocker control schematic. Just need a slight push of the the rocker,, you can see the four propellers get spun rapidly. Keep increasing the throttle, make sure it fly away. A little higher, don’t fly along the ground and then you can control the stability with the rocker bar. | ||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_Remote6.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *When you find the quadcopter can only fly along the ground and fail to fly higher even when you increase the throttle violently, it means the battery has run out of power. At this time, please charge the battery and avoid the accident. Since our fly-control backplane integrates battery management, you only need to charge the quadcopter with a USB cable. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Microduino_QuadCopter_Remote7.jpg||600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Before you turn off the quadcopter, please cut off the power of the quadcopter first and then turn off the power of the remote controller, otherwise the quadcopter may get out be control. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Attention== | ||
| + | *BT connection is the first and the key step. So please make sure the two BT modules connected successfully. | ||
| + | *Please don;t stack the BT module during the download for it will cause serial port conflict. | ||
| + | *Make the installation of the quadcopter’s four propellers, or it can’t fly. | ||
| + | *Please don’t get wrong of the electrode, or it will get the circuit burnt. | ||
| + | *Before flying, please adjust the Microduino-Joypad for it may lead to an unstable fly. | ||
| + | *Before the remote control and unlock, please pull down the top-left switch (Close the throttle) and adjust the throttle to the lowest before flying for fear that the throttle value is too large and causes accident. | ||
| + | *Before you turn off the quadcopter, please cut off the power of the quadcopter first and then turn off the power of the remote controller, otherwise the quadcopter may get out be control. | ||
| + | |} | ||
2014年9月4日 (四) 15:18的版本
目录개요
부품 리스트
참고문서
소개비행원리Quadcopter, also called a quadrotor helicopter, is similar to a helicopter, which can fly or be suspended in the air. Like a traditional helicopter, it adopts a main rotor to generate lift and a tail rotor to offset the torque generated by the main rotor (Namely head-locking). Different from that drive method, The diagonal motor of the quadcopter adopts the pros and cons propeller design. So it needs no extra framework to have heard-locking. As it is shown in the picture 1.1, the No. 1 and No. 3 propellers are a pair of diagonal pros and cons propellers, and the No. 2 and No.4 are another pair. When the rotational speed keeps the same, the torque generated by the pro propeller will offset the the torque generated by the cons propeller to keep the direction unchanged (As the arrow shows). In the schematic diagram, the most common quadcopter is the X-shaped. (There is also a kind of cross-like quadcopter, which is easy to recognize but has a poor mobility. ) Quadcopter can finish four basic motions including rise and fall, pitch, roll and yaw. Rise and fall means the aircraft goes up vertically. The rising process is achieved by four motors speeding up at the same time. So does the falling process. Pitch means the aircraft tilts forward or backward, which is achieved by speeding up the No.3 and No.4 motors. Roll is actually that the aircraft tilts leftwards or rightwards, achieved by speeding up the NO.2 and No. 3 motors. Yaw is the deviation of the aircraft’s head, which is achieved by speeding up the No. 2 and No.4 motors. Players can watch and have a better understanding during the process of installing and debugging the quadcopter. 구조The structure schematic diagram is shown below. The simplified system is consist of a remote control signal receiver, an aircraft controller and four motors. The remote control signal receiver converts the received signal to the format of PWM or PPM and send it the aircraft controller. The controller controls the four motors via PWM and achieves its expected motion according to the remote control signal it receives as well as the sensor value. It is necessary for the aircraft controller to contain the gyroscope and the accelerometer. The position of the quadcopter is calculated through the data acquired from the two sensors and controls the rotating rate through algorithm like PID after the calculation. Off cause, you can also locate the aircraft’s head adding an electronic compass and GPS to locate the quadcopter. To be simple, quadcopter is a closed-cycle control system with two loops--the bigger loop is input by a remote control receiver and the smaller one is input by the attitude sensor. For general fixed-wing model aircraft, the controller is not that necessary and some player won’t install it on the fixed-wing model aircraft. Different from that, the quadcopter is an underactuated system with three degrees of freedom and four control input, which needs a control system to take charge. Off cause, there are some tech details remaining to be designed in the process, such as the reading-in data of the sensor needed to be filtered and the PID algorithm of the pitch, roll and yaw acquired to be adjusted.
효고ㅗMicroduino adopts the unique U-shaped 27Pin interface standard(UPIN-27) with compact size (25.4mm X 27.95 mm) just like a quarter. All modules can be stacked together through UPIN-27, delivered ready to plug in. Microduino-Quadcopter only needs five functional modules and the 330 Rack Mont Kits recommended at the least to work. (Microduino-Core, Microduino-10DOF, Microduino-BT, Microduino-QuadCopter and Microduino-Joypad.) And you only need to stack them together, which is very simple.
쿼드콥터 만들고 디버깅하기하드웨어 조립하기
Fixate the flight-control backplane on the main frame and set a forward direction before you do that. (The default forward direction of the flight-control backplane is the open end direction of the UPin interface.) Fixate the Microduino-Quadcopter on the main frame. Fixate the four motor arms on the main frame and in the process, set the head direction as follows: Generally, we set the two orange rotors in the front and the other two black ones in the back so that we can tell the head direction by the color even when the aircraft flies far away. When doing this, you also need to pay attention to the right order of CW and CCW paddle.CW paddles are marked with an A on it and CCW paddles are marked with a B.CW paddles should be fixed at left-front and right-rear.CCW paddles should be fixed at right-front and left-rear. Attention:The installation methods are shown as follows: Fixate the four motors on the main frame. Then connect those connectors to the motherboard. Although we’ve tried our best to make sure everything’s good, it’s still recommend to check those wires--the white and red wires from motors should be connected to the pin marked with a cross(+).The following figure shows a finished work. Make Connection between Two BT ModulesSince we build the wireless remote control through Bluetooth, that makes the two BT modules indispensable. As to the connection method, you can refer to: [[How to Connect two Microduino-BT modules together]
Download & DebugAssemble Microduino-Core,Microduino-10DOF and Microduino-USBTTL on the motherboard as the following figure: Place the quadcopter on a flat surface then connect it to the computer via USB.Select Microduino Core (Atmega328P@16M,5V) in the Arduino IDE,then download the program. Run the config tool in the following path:MultiWiiConf\application.windows32\MultiWiiConf.exe Connect PC to QuadcopterClick the RECONNECT button to connect.The raw data and some graphs should be shown if everything’s okay. Adjust the SensorMake sure the quadcopter is on a flat surface,then click the CALIB_ACC button to calibrate accelerometer.DO NOT move the quadcopter in 5 secs.Then click the CALIB_MAG button to calibrate magnetometer.In the coming 30secs,please grab your quadcopter and rotate it in every axis repeatedly. Then click the WRITE button to save the data. By clicking SELLECT SETTING,various parameters can be set,and the quadcopter’s status will be shown. Set PID ParameterThe quadcopter use proportional-integral-derivative controller (PID controller) to control its movement. With a proper set of PID values,the quadcopter can fly smoothly and stably. We offer the sample PID config file,user can load it and fly the copter in a few minutes: click LOAD,then select file pkj.mwi to load the config file,finally click write to save. If you want to adjust the parameters yourself,just click on the green bar and hold it,then drag it left or right to adjust.For more info, please google Multiwii. Set Flight ModeTo enhance the experience,we recommend users set several flight modes.Different flight modes can be selected by toggle the switch on the remote.And by using different combinations many flight modes can be chosen.The recommended flight modes settings are shown as below.To set a flight mode,just toggle the switch as your wish and click on the mode you want(the cube).ANGLE mode is the most stable mode,starters can practice under this mode.Don’t forget to WRITE before unplug the quadcopter.For more info,please google Multiwii. When everything’s done,remove the Microduino-USBTTL.
Build & Debug the Remote ControllerHere we adopt Microduino-Joypad as the remote controller. Off cause, you need modules, such as Microduino-TFT, Microduino-Core, Microduino-USBTTL and Microduino-BT to build the remote controller.
Hardware Buildup
Debug the Software
Meantime, you also need the libraries below: _01_Microduino_TFT_GFX: https://github.com/Microduino/Microduino_Tutorials/tree/master/Microduino_Libraries/_01_Microduino_TFT_GFX _01_Microduino_TFT_ST7735 : https://github.com/Microduino/Microduino_Tutorials/tree/master/Microduino_Libraries/_01_Microduino_TFT_ST7735 _01_Microduino_TFT: https://github.com/Microduino/Microduino_Tutorials/tree/master/Microduino_Libraries/_01_Microduino_TFT _08_Microduino_Shield_Joypad:https://github.com/Microduino/Microduino_Tutorials/tree/master/Microduino_Libraries/_08_Microduino_Shield_Joypad
Test FlyDebug Microduino-Joypad
Debug the Quadcopter Frame
Overall Test
Attention
|