“MicroMV 跟色车”的版本间的差异
(→Microduino的代码准备) |
|||
| 第218行: | 第218行: | ||
=='''Microduino的代码准备'''== | =='''Microduino的代码准备'''== | ||
| + | 用来用串口接收数据并控制小车 | ||
<source lang="cpp"> | <source lang="cpp"> | ||
#include <Microduino_Protocol.h> | #include <Microduino_Protocol.h> | ||
2018年5月16日 (三) 06:56的版本
基本原理
- MicroMV捕捉对应颜色的物体获取坐标
- 通过串口发送给microduino
- microduino接收数据后控制小车
MicroMV的代码准备
把2017-10-16-find-ball-keep_shape_ok.py替换到MicroMV生成的U盘空间中的main.py做为主程序
2017-10-16-find-ball-keep_shape_ok.py:
import sensor, image, time,math
from pyb import UART
from pyb import LED
from pyb import Pin
uart = UART(4, 9600)
uart_buf = bytearray([0xaa,0xbb,0x33,0x44,0x0d,0x0a])
visual_angle=56
target_width_mm=0
target_height_mm=0
target_width=0
target_height=0
target_angle=0
target_angle_h=0
target_distance=0
target_distance_h=0
target_distance_w=0
target_shape_begin=1
left_speed=1500
right_speed=1500
rad=0.01745329
steering_scale=0
#threshold = (35, 75, 25, 75, 15, 60) #orange bowl(3D print,night)
#threshold = (45, 85, 0, 70, 40, 80) #pink ball(Flowerpot,day)
#threshold = (50, 80, 30, 70, 40, 75) #pink ball(Flowerpot,night)
#threshold = (65, 100, 30, 50, 5, 30) #Pumpkin toy
#threshold = (45, 75, 0, 40, -50, -10) #blue bowl(3D print)
#threshold = (40, 70, -35, -10, -5,20) #green bowl(3D print)
threshold = (50, 80, 30, 70, 40, 75) #key set
ROI=(110,80,100,100)
robot_buf = bytearray([0xaa,0xbb,0x01,0xdc,0x05,0xdc,0x05,0x00])
def robotTX():
#print("left:",left_speed,"right:",right_speed)
robot_buf[3]=int(left_speed)%256
robot_buf[4]=int(left_speed)//256
robot_buf[5]=int(right_speed)%256
robot_buf[6]=int(right_speed)//256
check_sum=1
check_sum^=4
check_sum^=robot_buf[3]
check_sum^=robot_buf[4]
check_sum^=robot_buf[5]
check_sum^=robot_buf[6]
check_sum%=256
robot_buf[7]=check_sum
uart.write(robot_buf)
def trackTarget():
global dir_mem
global left_speed
global right_speed
global area_max
global target_distance
if target_num!=0 and abs(target_x)<130:
if target_distance<50:
steering_scale=4
elif target_distance<100:
steering_scale=3
elif target_distance<150:
steering_scale=2
else:
steering_scale=1
left_speed=2000+target_x*steering_scale
right_speed=2000-target_x*steering_scale
if left_speed>2000:
left_speed=2000
elif left_speed<1000:
left_speed=1000
if right_speed>2000:
right_speed=2000
elif right_speed<1000:
right_speed=1000
if target_distance<50:
steering_scale=2
elif target_distance<100:
steering_scale=1
elif target_distance<150:
steering_scale=0.5
else:
steering_scale=0
left_speed-=abs(target_x*steering_scale)
right_speed-=abs(target_x*steering_scale)
if left_speed>2000:
left_speed=2000
elif left_speed<1000:
left_speed=1000
if right_speed>2000:
right_speed=2000
elif right_speed<1000:
right_speed=1000
if target_x>=0:
dir_mem=2
else:
dir_mem=1
if area_max>area_begin*0.7:
left_speed=1500
right_speed=1500
print("get target")
#print("x:",target_x,"y:",target_y,"left:",left_speed,"right:",right_speed)
elif target_num!=0:
if target_x>0:
left_speed=2000
right_speed=1500
else:
left_speed=1500
right_speed=2000
else:
print("No target")
if dir_mem==1:
left_speed=1200
right_speed=2000
else:
left_speed=2000
right_speed=1200
robotTX()
def carShake():
global left_speed
global right_speed
for a in range(0,2):
left_speed=1650
right_speed=1350
robotTX()
time.sleep(40)
left_speed=1350
right_speed=1650
robotTX()
time.sleep(40)
left_speed=1500
right_speed=1500
robotTX()
sensor.reset()
sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.RGB565)
sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QVGA)
sensor.skip_frames(time = 2000)
sensor.set_auto_gain(False) # must be turned off for color tracking
sensor.set_auto_whitebal(False) # must be turned off for color tracking
sensor.set_brightness(-3)
clock = time.clock()
dir_mem=0
target_x=0
target_y=0
area_begin=0
pin0 = Pin('SW', Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)
carShake()
while(pin0.value()):
img = sensor.snapshot()
statistics=img.get_statistics(roi=ROI)
img.draw_rectangle(ROI,color = (255, 0, 0))
print(statistics.l_mode(),statistics.a_mode(),statistics.b_mode())
threshold=(statistics.l_mode()-25,statistics.l_mode()+25,statistics.a_mode()-25,statistics.a_mode()+25,statistics.b_mode()-25,statistics.b_mode()+25)
carShake()
time.sleep(100)
carShake()
img = sensor.snapshot()
blobs =img.find_blobs([threshold], pixels_threshold=200, area_threshold=200, merge=True)
for blob in blobs:
if blob.area()>area_begin:
area_begin=blob.area()
width_begin=blob.w()
height_begin=blob.h()
target_angle=width_begin*visual_angle/320
target_angle_h=height_begin*visual_angle/360
target_width_mm=math.tan((target_angle/2)*rad)*240
target_height_mm=math.tan((target_angle_h/2)*rad)*240
target_shape_begin=width_begin/height_begin
print(target_angle)
print(target_width_mm)
while(True):
img = sensor.snapshot()
target_num=0
area_max=0
blobs =img.find_blobs([threshold], pixels_threshold=200, area_threshold=200, merge=True)
for blob in blobs:
img.draw_cross(blob.cx(), blob.cy())
target_num=target_num+1
if blob.area()>area_max:
area_max=blob.area()
target_x=blob.cx()-160
target_y=140-blob.cy()
target_width=blob.w()
target_height=blob.h()
for blob in blobs:
if blob.area()==area_max:
img.draw_rectangle(blob.rect())
target_angle=target_width*visual_angle/320
target_angle_h=target_height*visual_angle/360
target_distance_w=target_width_mm/2/math.tan((target_angle/2)*rad)
target_distance_h=target_height_mm/2/math.tan((target_angle_h/2)*rad)
target_shape=target_width/target_height
print("shape_begin:",target_shape_begin,"shape:",target_shape,"distance_w_mm",target_distance_w,"distance_h_mm",target_distance_h)
if target_shape_begin/target_shape>0.8 and target_shape_begin/target_shape<1.2:
target_distance=(target_distance_w+target_distance_h)/2
elif target_shape_begin/target_shape>=1.2:
target_distance=target_distance_h
else:
target_distance=target_distance_w
print("dis",target_distance)
trackTarget()
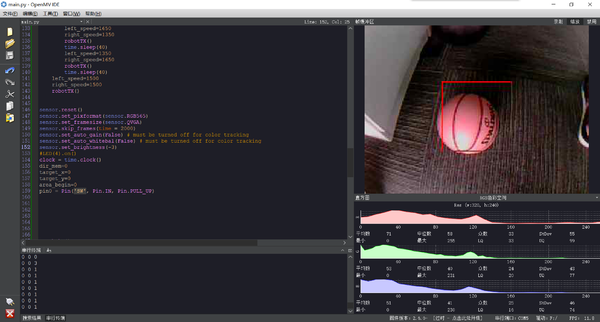
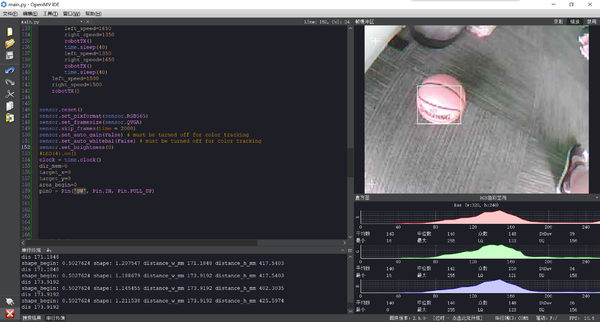
IDE运行效果为
初始阶段为学习阶段:屏幕中间有一个方框,把要识别的物体放到方框中,按住KEY_P3按键就记录下来了
接下来屏幕中有对应颜色物体就会用方框注明
Microduino的代码准备
用来用串口接收数据并控制小车
#include <Microduino_Protocol.h>
//Core UART Port: [SoftSerial] [D2,D3]
#if defined (__AVR_ATmega168__) || defined (__AVR_ATmega328__) || defined (__AVR_ATmega328P__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega32U4__)
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
SoftwareSerial mySerial(2, 3); /* RX:D2, TX:D3 */
#define ProSerial mySerial
#endif
//Core+ UART Port: [Serial1] [D2,D3]
#if defined(__AVR_ATmega1284P__) || defined (__AVR_ATmega644P__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega128RFA1__)
#define ProSerial Serial1
#endif
ProtocolSer protocol(&ProSerial, 4); //采用ProSerial,数据长度为16个字节
uint16_t recData[2];
uint8_t recCmd;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
protocol.begin(9600); //9600/19200/38400
}
void loop() {
if (protocol.available())
{
protocol.readWords(&recCmd, recData, 4);
Serial.println("protocol Received !");
Serial.print("recCmd: ");
Serial.print(recCmd);
Serial.print(" Data:");
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(recData[i]);
}
Serial.println();
car(recData[0], recData[1]);
}
}
void car(int _left, int _right) {
if (_left == 1500) {
digitalWrite(6, HIGH);
digitalWrite(8, HIGH);
}
else if (_left > 1500) {
_left = map(_left, 1500, 2000, 255, 0);
analogWrite(6, _left);
digitalWrite(8, HIGH);
}
else {
_left = map(_left, 1000, 1500, 255, 0);
analogWrite(6, _left);
digitalWrite(8, LOW);
}
if (_right == 1500) {
digitalWrite(5, HIGH);
digitalWrite(7, HIGH);
}
else if (_right > 1500) {
_right = map(_right, 1500, 2000, 255, 0);
analogWrite(5, _right);
digitalWrite(7, HIGH);
}
else {
_right = map(_right, 1000, 1500, 255, 0);
analogWrite(5, _right);
digitalWrite(7, LOW);
}
}