“时钟”的版本间的差异
(→调试) |
(→程序) |
||
| (未显示2个用户的3个中间版本) | |||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
| + | {{Language |Clock}} | ||
{| style="width: 800px;" | {| style="width: 800px;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 第7行: | 第8行: | ||
==设备== | ==设备== | ||
| − | *'''[[Microduino-Core]]''' | + | *'''[[Microduino-Core/zh]]''' |
| − | *'''[[Microduino- | + | *'''[[Microduino-USBTTL/zh]]''' |
| − | *'''[[Microduino-RTC]]''' | + | *'''[[Microduino-RTC/zh]]''' |
*其他硬件设备 | *其他硬件设备 | ||
| − | **USB数据连接线 一根 | + | **USB数据连接线 一根 |
==原理图== | ==原理图== | ||
| 第20行: | 第21行: | ||
==程序== | ==程序== | ||
| − | + | [https://github.com/Microduino/Microduino_Tutorials/tree/master/Microduino_Processing/ProcessingColock ProcessingColock] | |
| − | MicroduinoColock | + | [https://github.com/Microduino/Microduino_Tutorials/tree/master/Microduino_Processing/MicroduinoColock MicroduinoColock] |
==调试== | ==调试== | ||
2014年10月29日 (三) 07:26的最新版本
| Language | English |
|---|
目的本教程将教大家如何用processing来显示Microduino时钟。 设备
原理图堆叠设备说明中的三个Microduino模块即可 程序调试步骤一:按着原理图搭建硬件环境,像这样:
本例需要两端的代码,Processing端和Microduino端 Microduino: //运行RTC,并输出时间数据到串口 void loop()
{
rtc.formatDate();
rtc.formatTime();
//send time data to port
Serial.print(rtc.getHour());
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(rtc.getMinute());
Serial.print(":");
Serial.println(rtc.getSecond());
}
//初始化时间 //inital time
void vosettime()
{
//rtc.initClock();
//day, weekday, month, century(1=1900, 0=2000), year(0-99)
rtc.setDate(4, 1, 6, 0, 14);
//hr, min, sec
rtc.setTime(15, 28, 50);
}
Processing: //得到第一个串口的数据,并定义如果有换行就缓存 // List all the available serial ports in the output pane. // You will need to choose the port that the Wiring board is // connected to from this list. The first port in the list is // port #0 and the third port in the list is port #2. println(Serial.list()); // Open the port that the Wiring board is connected to (in this case #0) // Make sure to open the port at the same speed Wiring is using (9600bps) port = new Serial(this, Serial.list()[0], 9600);
int radius = min(width, height)/2; secR = radius * 0.72; minR = radius * 0.60; hourR = radius * 0.50; clockDiameter = radius * 1.8; cx = width /2 ; cy = height /2 ; //串口输出鼠标x坐标值,并绘制当前值 void update(int x)
{
port.write(x);
stroke(255);
line(mouseX, 0, mouseX, 160);
text (mouseX, mouseX, 180);
}
//split data by ":"
String time[]=val.split(":");
//if some exception happend, initial time is 0 colock
try {
hour=Integer.parseInt(time[0]);
minute=Integer.parseInt(time[1]);
second=Integer.parseInt(time[2]);
}
catch (NumberFormatException e) {
hour=0;
minute=0;
second=0;
}
//绘制钟表 float s = map(second, 0, 60, 0, TWO_PI) - HALF_PI;
float m = map(minute+norm(second, 0, 60), 0, 60, 0, TWO_PI)- HALF_PI;
float h = map(hour+norm(minute, 0, 60), 0, 24, 0, TWO_PI * 2 ) - HALF_PI;
//draw colock
stroke(255, 250, 0);
strokeWeight(1);
line(cx, cy, cx + cos(s) * secR, cy + sin(s) * secR);
strokeWeight(2);
line(cx, cy, cx+ minR * cos(m), cy + minR * sin(m));
strokeWeight(4);
line(cx, cy, cx + hourR * cos(h), cy + hourR * sin(h));
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(255, 0, 0);
for (int a = 0 ;a<360;a+=6) {
float angle = radians(a);
float cx1 = (secR+20) * cos(angle);
float cy1 = (secR+20) * sin(angle);
point(cx + cx1, cy + cy1);
if (a%30==0) {
line(cx+cx1, cy+cy1, cx+cx1*0.98, cy+cy1*0.98);
fill(255);
int mark;
if (a/30>9) {
mark = a/30 -9;
}
else
{
mark = a/30 +3;
}
text(mark, cx+cx1*1.05-5, cy+cy1*1.05+5);
}
fill(90, 155, 11);
text(hour+":"+minute+":"+second, cx-25, cy+100);
text("Microduino", cx-25, cy-100);
}
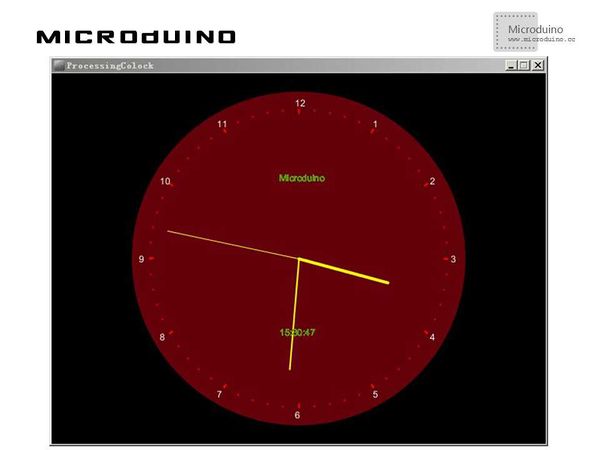
步骤三:下载代码并编译通过。 步骤四:运行后,看看processing中会出现什么。 结果屏幕上会显示一个运转的时钟,像这样
视频 |