“数码管控制”的版本间的差异
(→程序) |
(→Program) |
||
| (未显示2个用户的5个中间版本) | |||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
| + | {{Language |Digital_Tube_Control}} | ||
{| style="width: 800px;" | {| style="width: 800px;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | == | + | ==Objective== |
| − | + | The course will show you how to use Processing to control a common cathode digital tube. | |
| − | == | + | ==Equipment== |
| − | *'''[[Microduino-Core]]''' | + | *'''[[Microduino-Core/zh]]''' |
| − | *'''[[Microduino- | + | *'''[[Microduino-USBTTL/zh]]''' |
| − | * | + | *Other Hardware Equipment |
| − | ** | + | **A USB cable |
| − | ** | + | **A common cathode digital tube |
| − | ** | + | **A box of jumpers |
| − | ** | + | **A resistor of 10K Ω |
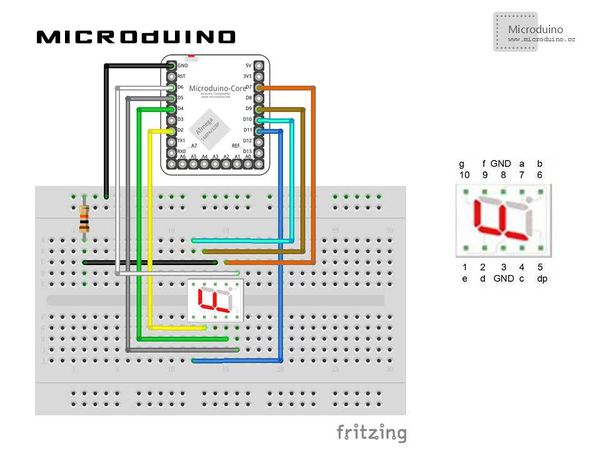
| − | == | + | ==Schematic== |
[[File:processing7SegmentSchematics.jpg|600px|center|thumb]] | [[File:processing7SegmentSchematics.jpg|600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Program== |
| − | https://github.com/Microduino/Microduino_Tutorials/tree/master/Microduino_Processing/ProcessingSegment | + | [https://github.com/Microduino/Microduino_Tutorials/tree/master/Microduino_Processing/ProcessingSegment ProcessingSegment] |
| − | == | + | ==Debugging== |
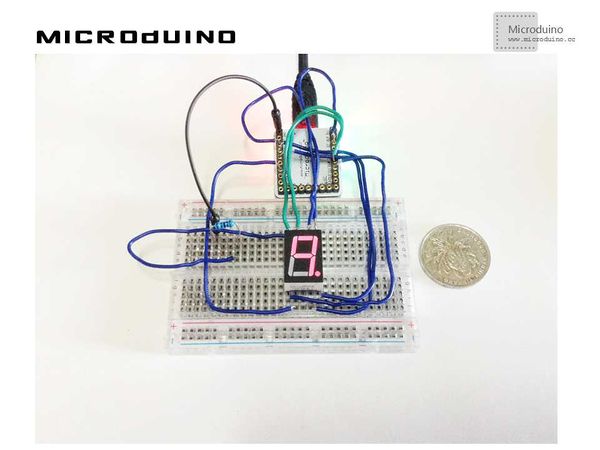
| − | + | Step 1:Build the hardware environment according to the schematic, just like this: | |
[[File:processing7SegmentConnectionDiagram.jpg|600px|center|thumb]] | [[File:processing7SegmentConnectionDiagram.jpg|600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| − | + | Step 2: Here is the code needed: | |
| − | + | The code the two ends(Processing and Microduino) | |
Microduino: | Microduino: | ||
| − | + | Using Firmata's StandardFirmata program. | |
Processing: | Processing: | ||
| − | // | + | //Define eight led lights to indicate a digital tube. |
LED[] leds = new LED[8]; // An array of 8 led objects! | LED[] leds = new LED[8]; // An array of 8 led objects! | ||
| − | // | + | //Define Microduino pins of the corresponding digital tube pins (1,2...10). |
int microduinoPins[] = {//Correspondence microduino pin for 7 segment | int microduinoPins[] = {//Correspondence microduino pin for 7 segment | ||
11,2,4,5,6,7,9,10}; | 11,2,4,5,6,7,9,10}; | ||
| − | // | + | //Define the name of each segment LED digital tube |
String segmentLables[]={"1-e","2-d","3-c","4-dp","5-b","6-a","7-f","8-g"}; | String segmentLables[]={"1-e","2-d","3-c","4-dp","5-b","6-a","7-f","8-g"}; | ||
| − | // | + | //Initialize and draw each led in setup(). |
for (int i = 0; i < leds.length; i ++ ) { // Initialize each led and output pin using a for loop. | for (int i = 0; i < leds.length; i ++ ) { // Initialize each led and output pin using a for loop. | ||
| − | |||
arduino.pinMode(microduinoPins[i], Arduino.OUTPUT); | arduino.pinMode(microduinoPins[i], Arduino.OUTPUT); | ||
} | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | leds[0] = new LED(50, 350, 50,200,1); | ||
| + | leds[1] = new LED(100, 550, 200,50,2); | ||
| + | leds[2] = new LED(300, 350, 50,200,3); | ||
| + | leds[3] = new LED(350, 550, 50,50,4); | ||
| + | leds[4] = new LED(300, 100, 50,200,5); | ||
| + | leds[5] = new LED(100, 50, 200,50,6); | ||
| + | leds[6] = new LED(50, 100, 50,200,7); | ||
| + | leds[7] = new LED(100, 300, 200,50,8); | ||
| − | // | + | //Draw the digital tube in draw(), judge the status of the led lights, and send the current status to Microduino |
for (int i = 0; i < leds.length; i ++ ) { // Run each Car using a for loop. | for (int i = 0; i < leds.length; i ++ ) { // Run each Car using a for loop. | ||
leds[i].display(); | leds[i].display(); | ||
//draw segemnt lables | //draw segemnt lables | ||
| − | text (segmentLables[i], | + | text (segmentLables[i], leds[i].xpos, leds[i].ypos); |
if (leds[i].button) {//switch led on/off | if (leds[i].button) {//switch led on/off | ||
| 第73行: | 第82行: | ||
} | } | ||
| − | + | Step 3:Download the code and get it compiled successfully. | |
| − | + | Step 4:There will appear eight led lights in Processing after the system goes smoothly. Please click each led and see the response of the digital tube. | |
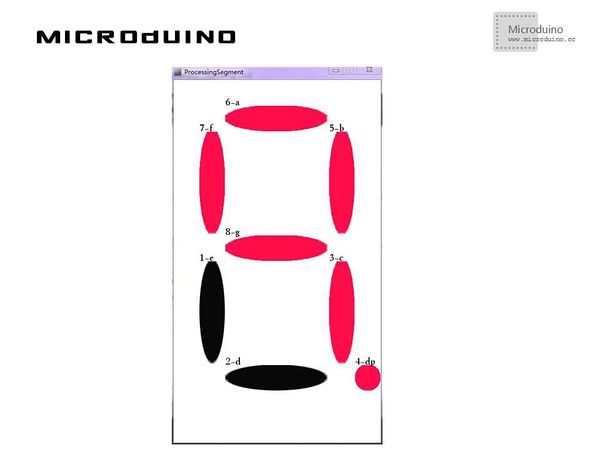
| − | == | + | ==Result== |
| − | + | Click the mouse and the corresponding digital tube led will turn on or off, as follows: | |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:processing7SegmentResult1.jpg|600px|center|thumb]] |
| − | + | ==Video== | |
| − | == | ||
|} | |} | ||
2014年10月29日 (三) 07:25的最新版本
| Language | English |
|---|
ObjectiveThe course will show you how to use Processing to control a common cathode digital tube. Equipment
SchematicProgramDebuggingStep 1:Build the hardware environment according to the schematic, just like this:
The code the two ends(Processing and Microduino) Microduino: Using Firmata's StandardFirmata program. Processing: //Define eight led lights to indicate a digital tube. LED[] leds = new LED[8]; // An array of 8 led objects! //Define Microduino pins of the corresponding digital tube pins (1,2...10). int microduinoPins[] = {//Correspondence microduino pin for 7 segment
11,2,4,5,6,7,9,10};
//Define the name of each segment LED digital tube String segmentLables[]={"1-e","2-d","3-c","4-dp","5-b","6-a","7-f","8-g"};
for (int i = 0; i < leds.length; i ++ ) { // Initialize each led and output pin using a for loop.
arduino.pinMode(microduinoPins[i], Arduino.OUTPUT);
}
leds[0] = new LED(50, 350, 50,200,1);
leds[1] = new LED(100, 550, 200,50,2);
leds[2] = new LED(300, 350, 50,200,3);
leds[3] = new LED(350, 550, 50,50,4);
leds[4] = new LED(300, 100, 50,200,5);
leds[5] = new LED(100, 50, 200,50,6);
leds[6] = new LED(50, 100, 50,200,7);
leds[7] = new LED(100, 300, 200,50,8);
//Draw the digital tube in draw(), judge the status of the led lights, and send the current status to Microduino for (int i = 0; i < leds.length; i ++ ) { // Run each Car using a for loop.
leds[i].display();
//draw segemnt lables
text (segmentLables[i], leds[i].xpos, leds[i].ypos);
if (leds[i].button) {//switch led on/off
arduino.digitalWrite(microduinoPins[i], Arduino.HIGH);
}
else {
arduino.digitalWrite(microduinoPins[i], Arduino.LOW);
}
}
Step 3:Download the code and get it compiled successfully. Step 4:There will appear eight led lights in Processing after the system goes smoothly. Please click each led and see the response of the digital tube. ResultClick the mouse and the corresponding digital tube led will turn on or off, as follows: Video |